Nimble Reputations
Context
Nimble's reputation system secures the network with efficient AI task matching. Each GPU miner has a reputation score that reflects their historical AI task completions and any fraudulent behaviors. The more legitimate work completed, the higher the reputation score. Conversely, the more fraudulent behaviors detected, the lower the reputation score. More mined and staked tokens also lead to a higher reputation score.
New Miners
Initially, new miners are granted a small reputation score. They are assigned AI tasks based on this score during a slow-start period (currently 14 days). After this period, miners with no AI task completions receive a zero reputation score. Fraudulent miners receive negative reputation scores, and their Nimble mining rewards are slashed, while miners with high AI task completion rates enjoy boosted reputation scores.
Understanding Miners' Reputation Score
To ensure high-quality work from miners, Nimble leverages an evaluation flow that utilizes various techniques, such as using the MD5 hash of trained model snapshots and comparing loss values with Nimble's pretrained models. The result of this evaluation process is a boolean decision that determines whether a miner’s work is legitimate or fraudulent.
For bootstrap historical data associated with a given miner’s wallet address, we have the following metrics:
Total Number of Tasks Received by a Miner
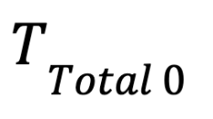
Total Number of Tasks Recognized as Cheating

Total Number of Tasks Recognized as Good

Total Nimble Token Received
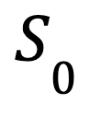
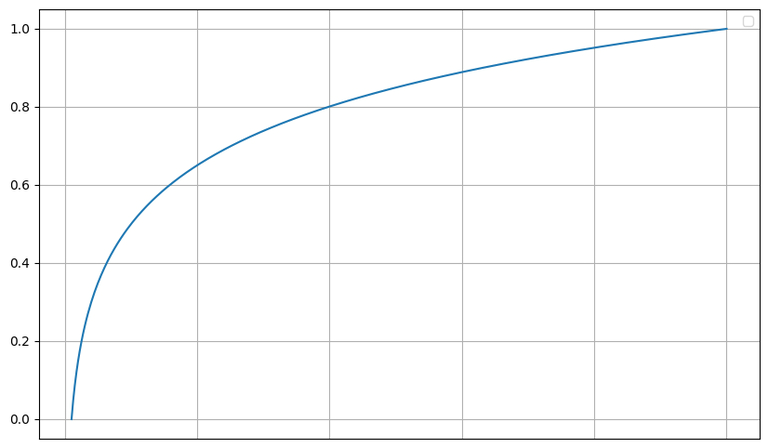
Based on total number of tasks recognized as Good
A miner’s reputation score RS depends on:
- Total Staked token
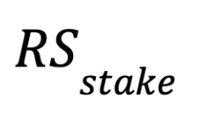
- Total Nimble Token Received
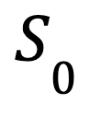
- Cheat ratio
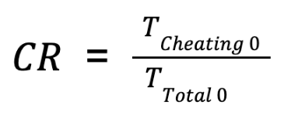
- Base Reputation Score
- This score is based purely on the ratio of good tasks to cheating tasks.
- Impact Factor IF
The Impact Factor
The Impact Factor represents a miner’s historical behavior, and will influence the miner’s chances of getting the task.
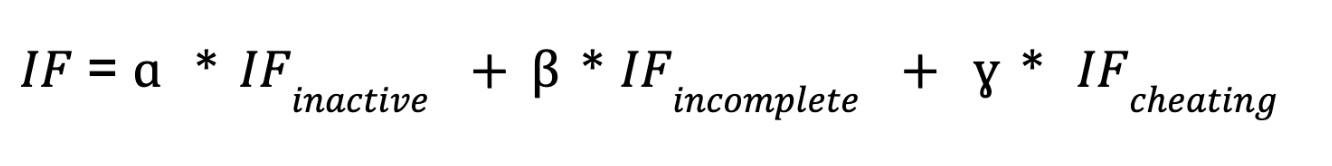
ɑ, β, ɣ are the factors that emphasize the miner’s normalized Slashing Factor.
- Inactive
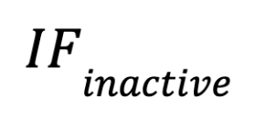
When a miner turns off their machine, their chances of receiving tasks decrease the next time they restart it.
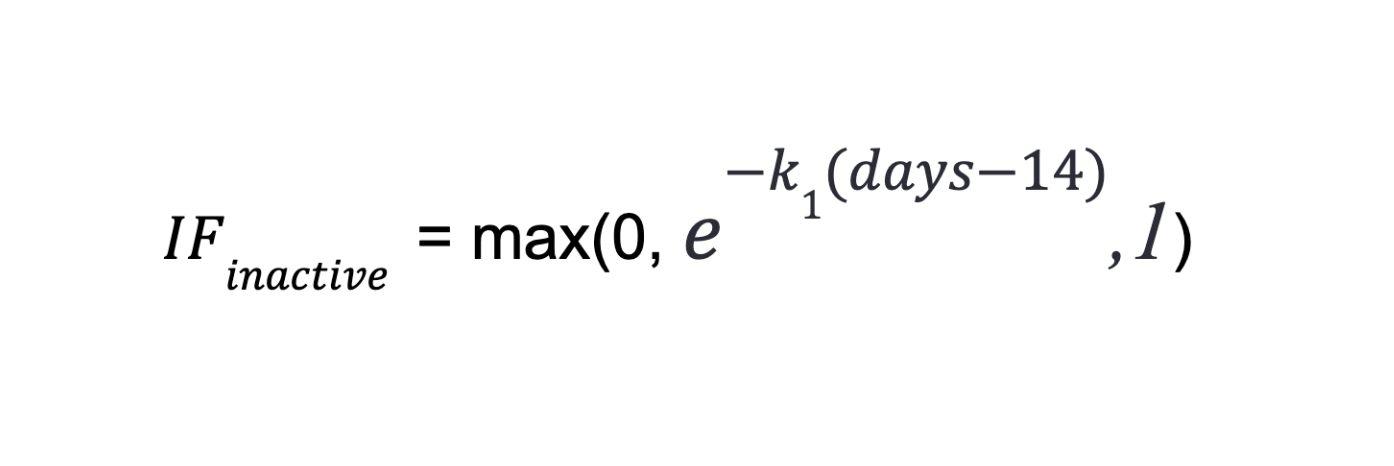
Where 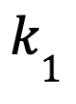 is the factor that emphasizes the miner’s normalized
is the factor that emphasizes the miner’s normalized 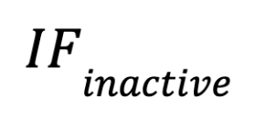
- Incomplete
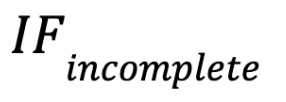
If miners fail to complete a task on time, their chances of receiving future tasks are reduced.
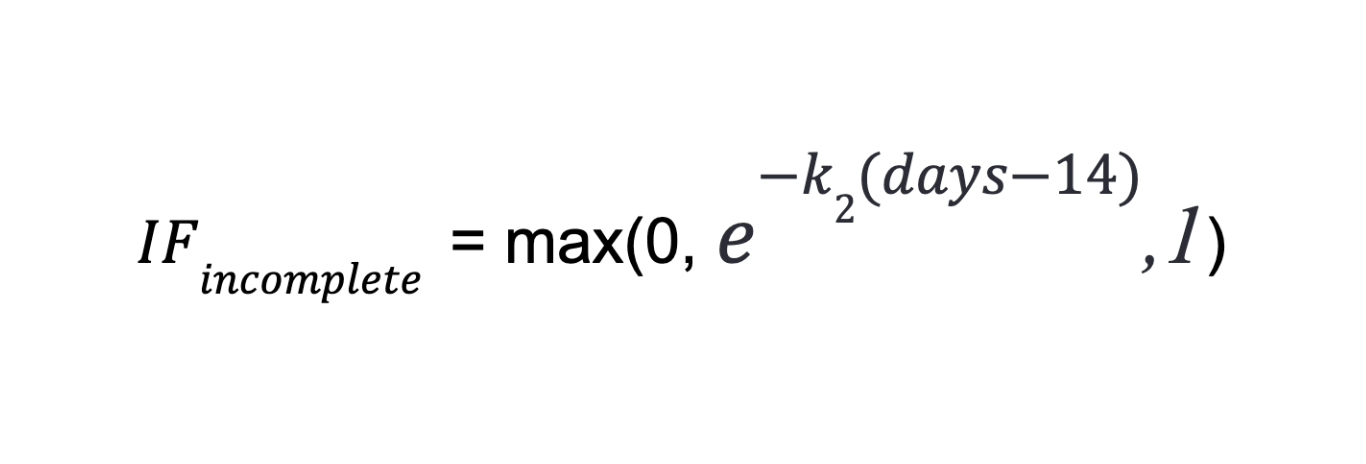
Where 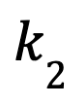 is the factor that emphasizes the miner’s normalized
is the factor that emphasizes the miner’s normalized 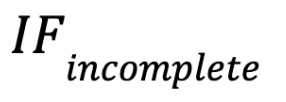
- Cheating

Based on the miner's track record, if their performance falls short compared to other miners, their chances of being assigned future tasks decrease.
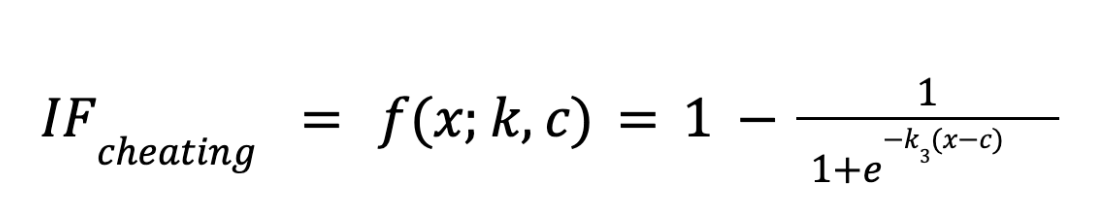
Where 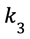 is the factor that emphasizes the miner’s normalized
is the factor that emphasizes the miner’s normalized 
The  is based on the ratio of the amount of the miner's cheating to the amount of all miners in the previous mining period, such as the median, 80%, 95% positions.
is based on the ratio of the amount of the miner's cheating to the amount of all miners in the previous mining period, such as the median, 80%, 95% positions.
p95: red p80: yellow p50: blue
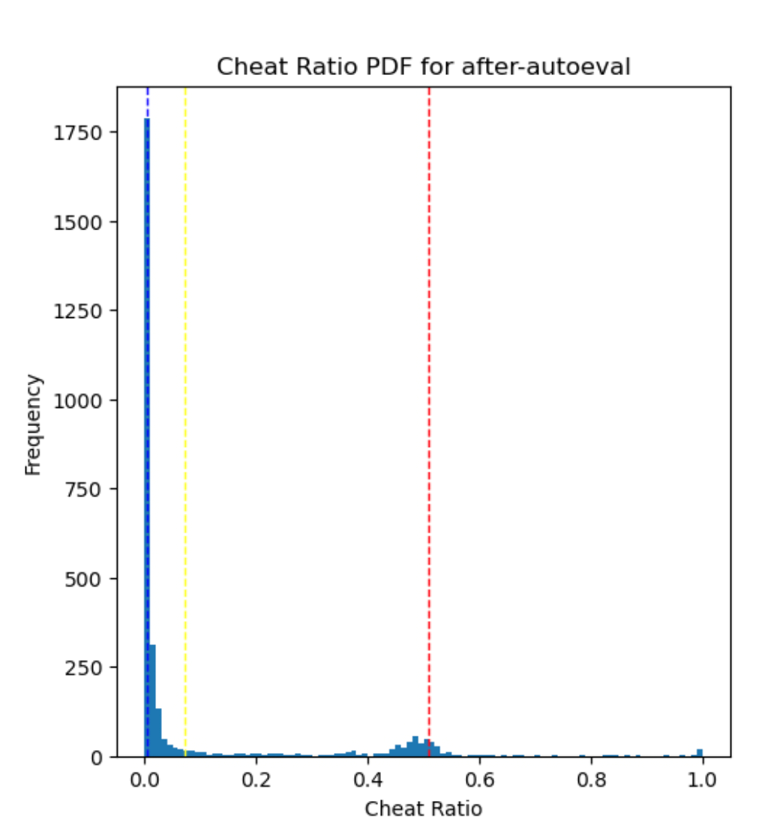
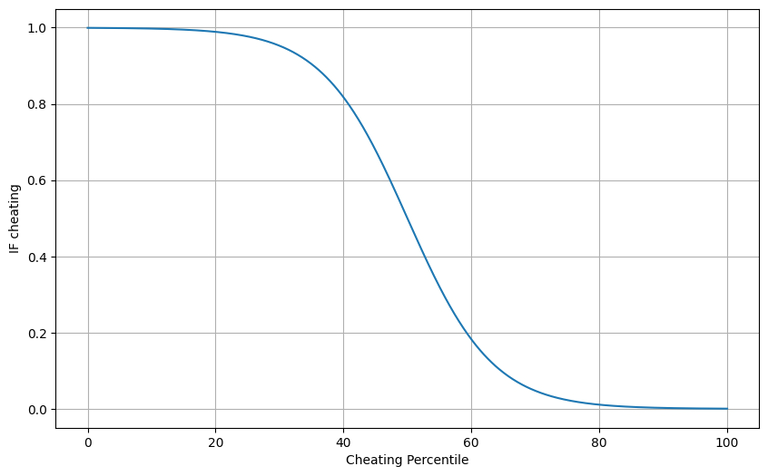
0 means he has never cheated, 100 means he is the most cheating among all miners.
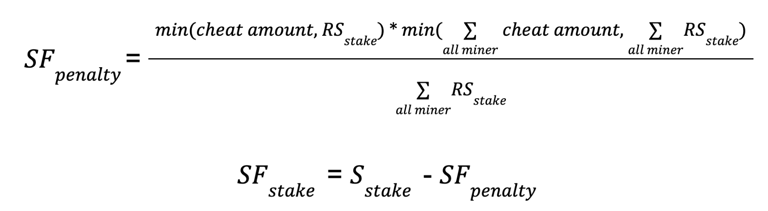
Slashing
Mined tokens are automatically staked for miners, but miners can also stake additional tokens to increase their reputation score. Fraudulent mining behavior results in a lower reputation score and slashed tokens.
- Penalty: $$SFpenalty$$
Understanding Mining Power
Mining power captures the full mining capacity of miners, reflecting their ability to run AI tasks at full GPU capacity. Each miner’s mining power consists of two components:
- Physical Mining Power: Miners can increase their physical mining power by adding more GPUs or using higher-end GPUs.
- Virtual Mining Power: Miners can also increase their total mining power by purchasing virtual mining power, which provides equivalent mining rewards as physical mining machines.
AI Task Distribution and Dynamic Rewards
AI tasks are distributed to miners through the AI orderbook based on their reputation score and mining power. The higher the reputation score, the better the chances of receiving AI tasks and, consequently, higher rewards. Miners with low reputation scores may not receive enough AI tasks to utilize their GPUs at full capacity, even if their mining power is high.
Miners can further enhance their reputation scores by completing more AI tasks and/or staking more Nimble tokens.
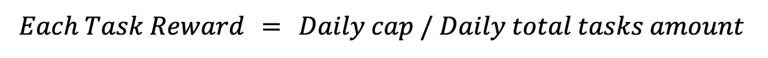
Maintaining high reputation scores is in miners' interests to secure higher mining rewards and avoid penalties for fraudulent behavior. Rewards are dynamic and depend on the network state, including AI task demand and GPU supply. Each task is tied to a specific mining reward, and the total rewards depend on the number of AI tasks completed and their associated rewards.